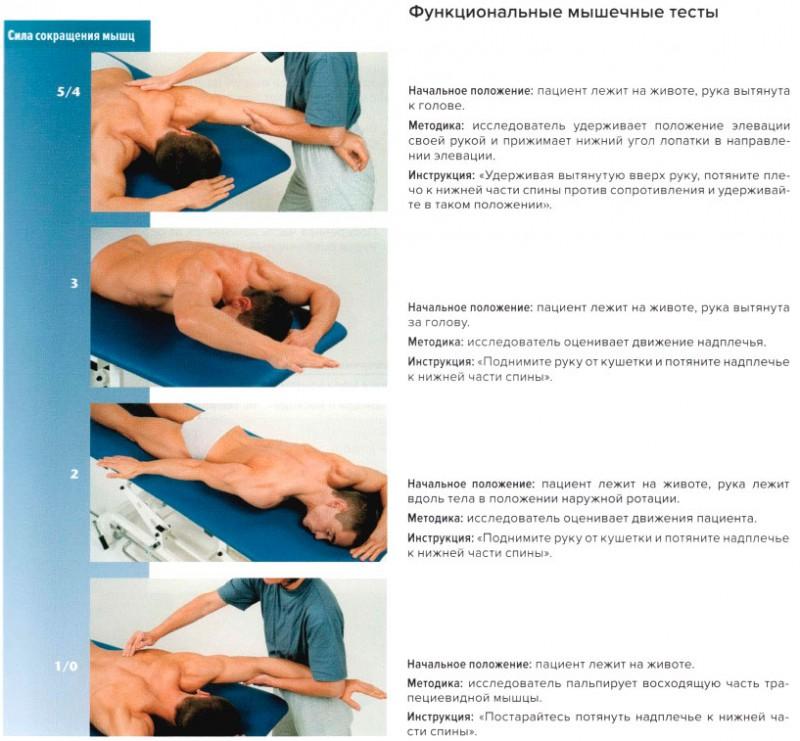
Подвздошно-поясничная мышца: упражнения на растяжку
Содержание:
- Clinical Importance of Psoas Muscle:
- References
- Relations
- Notes
- Оперативное лечение
- Симптомы заболевания
- Clinical significance
- «Мышца души»
- Участие в спорте[править | править код]
- Растяжка поясничной мышцы: комплекс на 2 минуты
- Function
- Расположение и структура поясничной мышцы
- Особенности мышц поясничного отдела
- Structure
- Functions
- Palpation
Clinical Importance of Psoas Muscle:
Relatively the conditions that involve psoas muscles are less common. However, a number of conditions that occurs involving iliac and psoas muscles, which includes infectious (particularly psoas abscess), haemorrhage, neoplastic lesions and injuries that take place due to trauma and during surgical procedures.
Psoas Syndrome and Iliopsoas Tendinitis:
Psoas syndrome and iliopsoas tendinitis are less common musculoskeletal conditions therefore, they often go misdiagnosed. Clinically it presents symptoms like low back pain, pain in groin and pelvis, radiating pain towards knee; which halts the primary function of psoas muscle that is hip flexion (hence difficult walking) and to sustain fully erect posture. The condition is mostly found in acute/overuse injuries, more commonly sports specific like runners, athletic activities, plyometric and among ballet dancers. It is known as internal coxa saltans.
Prolong sitting and work which requires long sitting periods, tend to put psoas in shortened and tight position leading to psoas syndrome. Because they are major flexors, weak psoas muscles can cause many of the surrounding muscles to compensate and become overused. That is why a tight or overstretched psoas muscle could cause low back and pelvic pain. Iliopsoas tendinitis may also cause snapping hip syndrome which is characterised by pain and snap (click) in groin.
Moreover, restriction of diaphragm can also occur due to psoas dysfunction and psoas spasm can potentially cause more disability of back muscles than other pathologic condition. A tight psoas muscle can create a thrusting forward of the ribcage. This causes shallow, chest breathing, which limits the amount of oxygen taken in and encourages over usage of your neck muscles.
‘Psoas, “the muscle of soul”
So, psoas may seem like small muscle, but its pivotal role in walking, postural alignment, balance, flexibility, joint mobility and organ functioning, makes it, clinically important, during assessment and screening.
References
- Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000. www.bartleby.com/107/.
- ↑
- Sandy Sajko, Kent Stuber. Psoas Major: a case report and review of its anatomy, biomechanics, and clinical implications. J Can Chiropr Assoc. 2009 Dec; 53(4): 311–318.
- Tonolini M, Campari A, Bianco R. Common and Unusual Diseases Involving the Iliopsoas Muscle Compartment: spectrum of cross-sectional imaging findings. Abdom Imaging. 2012; 37(1).
- Tufo A, Desai GJ, Cox WJ. Psoas syndrome: a frequently missed diagnosis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012 Aug;112(8):522-8
- Tufo A, Desai GJ, Cox WJ. Psoas syndrome: a frequently missed diagnosis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2012 Aug;112(8):522-8
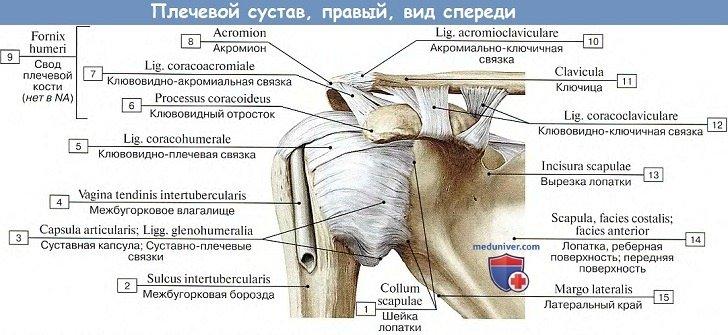
Relations

Psoas Major: Relations
The psoas major is the key muscle of the posterior abdominal wall, because its relationships supply a rational notion about the layout of structures in this region:
Lumbar plexus creates inside the substance of psoas. The plexus can be shown only by ripping the muscle, for it will not break up the muscle into planes.
5 nerves appear from underneath the lateral border of the psoas major from above downward; these are as follows:
- Subcostal nerve.
- Iliohypogastric nerve.
- Ilioinguinal nerve.
- Lateral cutaneous nerve of thigh.
- Femoral nerve.
The upper 4 nerves come above the iliac crest and runs downward and laterally across the quadratuslumborum muscle. The final nerve (femoral nerve) comes below the iliac crest and runs down in the groove between the psoas and iliacus muscles.
1 nerve (genitofemoral nerve) runs downward on the very front of the psoas major and occasionally may be mistaken for the tendon of psoas minor muscle.
3 significant structures being located on the medial side of the psoas major. From medial to lateral side these are: (a) lumbosacral trunk, (b) iliolumbar artery, and (c) obturator nerve.
Lumbosacral Triangle of Marcille

Psoas Major: Lumbosacral Triangle of Marcille
Psoas major’s a triangular separation on every side of the body of L5 vertebra with all the apex directed upward. It’s bounded medially by the body of L5 vertebra, laterally by the medial border of the psoas major, and inferiorly (base) by the ala of the sacrum. The apex is composed by the junction of psoas and the body of L5 vertebra. The floor (posterior wall) is composed by the transverse process of L5 vertebra and iliolumbar ligament.
It includes 4 structures. From medial to lateral sides, these are:
- Sympathetic trunk.
- Lumbosacral trunk.
- Iliolumbar artery.
- Obturator nerve.
Notes
Gray’s Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Platzer (2004), p 234
- Bojsen-Møller, Finn; Simonsen, Erik B.; Tranum-Jensen, Jørgen (2001). Bevægeapparatets anatomi [Anatomy of the Locomotive Apparatus] (in Danish) (12th ed.). pp. 261–266. ISBN 978-87-628-0307-7.
- Gray’s anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice. Standring, Susan (41st ed.). . 2016. p. 1324.e2. ISBN . OCLC .
- Earls, J., Myers, T (2010). Fascial Release for Structural Balance. Chchester, England: Lotus Publishing. p. 130. ISBN .
- Thieme Atlas of Anatomy (2006), p 422
- Akuthota, et all(2008). p 40
- Corbo, & Splittberger (2007). Your Body, Your Responsibility. Arizona: Wheatmark Inc, Amazon. p. 88.
Оперативное лечение
Лечение псоас-абсцессов оперативное. То есть проводится операция по хирургическому вскрытию гнойника. Одно лишь консервативное лечение тут невозможно по той причине, что с его помощью не получится вывести гной, прочистить мышцу и близлежащие к ней ткани и органы от омертвевших клеток.
Полость промывают от гнойной материи, после чего ее обрабатывают специальными препаратами-антисептиками. Устанавливаются специальные дренажи. В случае с псоас-абсцессом реабилитация после операции будет включать в себя прием антибиотиков, выписанных доктором.
Если характеризовать операцию в общем, то это вскрытие и дренирование сформировавшего абсцесса. Его вскрывают двумя способами: лоботомическим или же через брюшную переднюю стенку с правой или левой стороны. Это зависит от локализации воспаления на уровне гребней подвздошных костей. Брюшину отслаивают к средней линии.
Симптомы заболевания
Представим основные симптомы псоас-абсцесса:
- Боль в нижней половине живота.
- Ощущение дискомфорта в области паха, а также передней части бедра.
- Боль в нижней части спины.
- При разгибании ноги в области тазобедренного сустава чувствуется боль.
- Высокая температура тела, озноб, лихорадка.
Человек будет жаловаться на постоянную боль в левой или правой половине нижней части живота. Болевой синдром может ощущаться в них и одновременно. Нередко появляется дискомфорт в передней части бедра. При определенном распространении инфекции он переходит и в область паха. Это ощущается, как напряжение мышцы в зоне бедра. Что касается паха, больной будет отмечать будто бы скопление какого-то вещества.
При ходьбе также может чувствоваться боль, которая отдает уже в область спины. Лихорадка, высокая температура — это общие признаки активного воспалительного процесса в организме.
Состояние опасно тем, что клиническая картина в большинстве случаев является стертой. Особенно на фоне приема пациентом нестероидных противовоспалительных лекарств, которыми человек пытается заглушить боль. Пациент может длительно наблюдаться у невролога, в то время как причина болевого синдрома определена неверно.

Clinical significance
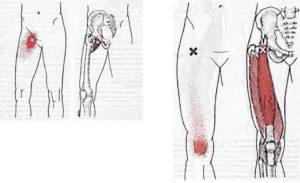
Tightness of the psoas can result in spasms or lower back pain by compressing the lumbar discs. A hypertonic and inflamed psoas can lead to irritation and entrapment of the ilioinguinal and the iliohypogastric nerves, resulting in a sensation of heat or water running down the front of the thigh.
Psoas can be palpated with active flexion of the hip. A positive psoas contracture test and pain with palpation reported by the patient indicate clinical significance. Care should be taken around the abdominal organs, especially the colon when palpating deeply.
The appearance of a protruding belly can visually indicate a hypertonic psoas, which pulls the spine forward while pushing the abdominal contents outward.
The psoas lies postero-lateral to the lumbar sympathetic ganglia, and the needle tip will often pass through the psoas major during a lumbar sympathetic block.
The genitofemoral nerve is formed in the midsection of the psoas muscle by the union of branches from the anterior rami of L1 and L2 nerve roots. The nerve then courses inferiorly within the psoas muscle and finally «pierces» the muscle and emerges on the anterior surface of the psoas distally. The nerve then traverses the retroperitoneum, descending over the anterior surface of the psoas.
«Мышца души»
Поясничная мышца – это сильнейшая мышца-стабилизатор, которая соединяет позвоночник и бедра, проходя в области тазобедренного сустава. В здоровом состоянии поясничная мышца оказывает амортизирующее действие между ногами и торсом, как подвеска.
Поясничная мышца также соединяется с диафрагмой, а значит, она может регулировать дыхание, а также вызывать ощущения страха и беспокойства и отвечать на них. Кроме того, существует прямая взаимосвязь между поясничной мышцей и мозжечковой миндалиной, участком мозга, который отвечает за рефлекс «бей или беги» и иногда называется «рептильным» мозгом. Вот что пишет по этому поводу Лиз Кох:
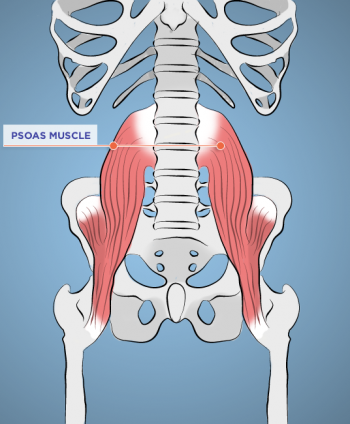
Также она заверяет, что как только мы научимся взаимодействовать с жизнью вне состояния хронического напряжения, поясничная мышца начнет расслабляться сама по себе: вот тогда мы сможем войти в состояние внутреннего спокойствия и четко настраиваться на ощущения, будь то настоящее спокойствие или опасность.
Участие в спорте[править | править код]
Прямая мышца живота выполняет динамическую работу при занятиях всеми видами спорта, где требуется сгибание туловища (прыжки в длину и в высоту, с шестом, тройные прыжки, художественные и спортивные прыжки в воду, спортивная гимнастика, гребля, футбол, метание копья, контактные виды спорта (бокс, дзюдо)]. Она также выполняет статическую работу при стабилизации туловища в выпрямленном положении в тяжелой атлетике, спортивной гимнастике и многих
других видах спорта. Она активно сокращается при удерживании туловища в санном спорте и при получении ударов в боксе.
|
Вид спорта |
Движения/удержание |
Функция |
Нагрузка |
Типы сокращений |
|
Прыжки в длину, Участвует в поднимании в высоту, с шестом, обеих ног при наклоне тройные прыжки таза назад |
Сгибание туловища |
Быстрая, взрывная |
Динамические концентрические |
|
|
Художественные и спортивные прыжки 8 воду, спортивная гимнастика |
Прижатие ног к туловищу при прыжке |
Сгибание туловища |
Быстрая, взрывная |
Динамические концентрические |
|
Раскачивание на перекладине,брусьях, разновысоких брусьях; угол сидя, подъем махом вперед на перекладине |
Сгибание туловища |
Быстрая, взрывная, силовая выносливость |
Динамические концентрические |
|
|
Бросок |
Сгибание туловища |
Быстрая, взрывная |
Динамические концентрические |
|
|
Различные виды спорта, например спортивная гимнастика, тяжелая атлетика, бокс, фехтование, горные лыжи, конькобежный спорт, настольный теннис |
Удержание туловища в выпрямленном положении |
Сгибание туловища |
Силовая выносливость |
Статические |
|
Бокс, карате |
Получение удара, нанесение удара |
Сгибание туловища |
Быстрая, взрывная |
Статические |
Растяжка поясничной мышцы: комплекс на 2 минуты
Если вас беспокоит напряжение в тазобедренной области, то необходимо просто растянуть поясничную мышцу и раскрыть бедренные сгибающие мышцы. См. видео (на англ. языке): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y0zqeh5wxWE
https://youtube.com/watch?v=Y0zqeh5wxWE
Лиз Кох также рекомендует положение под названием «конструктивный покой», с помощью которого можно удлинить и расслабить поясничную мышцу. В этом положении позвоночник прилегает к полу, и таким образом принимает свою естественную форму. Кроме того, это упражнение снимает напряжение и стресс, как физически, так и психологически. Делайте это упражнение 10-20 минут каждый день перед ужином, при этом расслабьте мышцы челюсти и позвольте глазам отдохнуть.
На первый взгляд оно кажется простым, но эта простота обманчива. В этом упражнении вес нашего тела используется таким образом, чтобы поясничная мышца расслабилась сама по себе. В результате, по мере регулярных тренировок вы сможете ощутить настоящее умиротворение и единение с миром.
Материалы в тему:
Доктор Бубновский: лечиться нужно движением, а не лекарствами
Положительные свойства йоги для вашего ума и тела
Физические упражнения являются важной частью профилактики и лечения рака
Как можно бороться с проблемами сердца, болезнью Альцгеймера и раком
Хронологический возраст – не самый лучший показатель вашего здоровья
Закаливание снижает воспаление, укрепляет иммунную систему, улучшает вывод токсинов и способствует долголетию
Многочисленные преимущества глубокой релаксации для здоровья
Целительная сила Природы
Рекомендуем прочесть нашу книгу:
Диагноз – рак: лечиться или жить? Альтернативный взгляд на онкологию
Чтобы максимально быстро войти в тему альтернативной медицины, а также узнать всю правду о раке и традиционной онкологии, рекомендуем бесплатно почитать на нашем сайте книгу «Диагноз – рак: лечиться или жить. Альтернативный взгляд на онкологию»
Читать бесплатно
Мы распространяем правду и знания. Если вы считаете нашу работу полезной и готовы оказать финансовую помощь, то вы можете перевести любую посильную для вас сумму. Это поможет распространению правдивой информации о раке и других болезнях и может спасти чьи-то жизни
Участвуйте в этом важном деле помощи людям!
Поддержать проект
Function
The psoas major joins the upper body and the lower body, the axial to the appendicular skeleton, the inside to the outside, and the back to the front. As part of the iliopsoas, psoas major contributes to flexion in the hip joint. On the lumbar spine, unilateral contraction bends the trunk laterally, while bilateral contraction raises the trunk from its supine position. In addition, attachment to the lesser trochanter, located on the postero-medial aspect of the femur, causes lateral rotation and weak adduction of the hip.
It forms part of a group of muscles called the hip flexors, whose action is primarily to lift the upper leg towards the body when the body is fixed or to pull the body towards the leg when the leg is fixed.
For example, when doing a sit-up that brings the torso (including the lower back) away from the ground and towards the front of the leg, the hip flexors (including the iliopsoas) will flex the spine upon the pelvis.
Owing to the frontal attachment on the vertebrae, rotation of the spine will stretch the psoas.
Расположение и структура поясничной мышцы
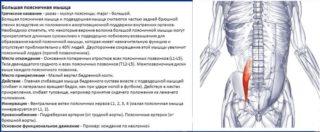 Большая мышца поясничного отдела берет свое начало от поперечных отростков позвонков. Крепится к 12-му грудному позвонку и ко всем поясничным позвонкам. Затем мускул спускается к тазобедренной части и крепится к малому вертелу бедренной кости.
Большая мышца поясничного отдела берет свое начало от поперечных отростков позвонков. Крепится к 12-му грудному позвонку и ко всем поясничным позвонкам. Затем мускул спускается к тазобедренной части и крепится к малому вертелу бедренной кости.
Musculus psoas major — единственное связующее звено в мышечной системе между туловищем и ногами. Она проходит от верхней части бедренной кости до внутреннего края подвздошной кости.
Поверхностный слой поясничной мышцы от глубокого отделяет поясничное сплетение. В нём сосредоточены многочисленные нервные окончания. Отсюда нервные импульсы передаются в бедренные мышцы, поперечную и косые мышцы живота, глубокие вращатели бедра и тазовое дно.
Особенности мышц поясничного отдела
В медицинской практике вокруг большой поясничной мышцы до сих пор разгораются споры и разногласия. Заблуждения о её строении и функциях формировались десятилетиями, поэтому учёным сложно развенчать устаревшие данные и неправдивые гипотезы.
Доказанные особенности крупнейшего мускула поясничного отдела:
- отвечает за пластику, грациозность;
- сгибание мышцы в тазобедренном суставе приводит в действие бедро;
- нервную иннервацию обеспечивает поясничное сплетение;
- служит ключом к красивой осанке и укреплению мышц кора;
- обеспечивает контакт с глубочайшим центром.
Для поддержания эластичности и упругости поясничной мышцы необходимо регулярно делать физические упражнения, спать на ортопедической поверхности и заботиться о комфорте спины в течение дня.
Укорочение большой поясничной мышцы
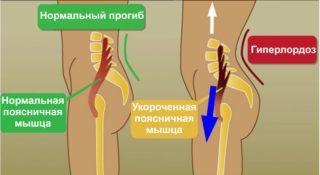 Проявлением заболевания служит искривление поясничного отдела позвоночника. Характерные симптомы:
Проявлением заболевания служит искривление поясничного отдела позвоночника. Характерные симптомы:
- выпячивание живота при наклоне таза вперед;
- глубокий изгиб поясницы;
- выпирающая грудная клетка.
Проблемой чаще всего страдают офисные работники. Причиной становится длительное сидение, неактивный образ жизни, неправильная осанка. Также на здоровье спины негативно сказываются стрессы, пагубные привычки.
Растяжение большой поясничной мышцы
Излишнее растяжение, как и укорочение, не является нормой и негативно влияет на двигательную функцию. Определить патологию можно по отсутствию изгиба поясницы. Другие симптомы:
- слабые боли в области позвоночника;
- иррадирование боли в бедро;
- внезапные приступы сильной боли.
Как правило, дискомфорт усиливается при хождении или длительном стоянии. Во время отдыха неприятные ощущения проходят, но ненадолго.
Structure
The psoas major is divided into a superficial and deep part. The deep part originates from the transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae I-V. The superficial part originates from the lateral surfaces of the last thoracic vertebra, lumbar vertebrae I-IV, and from the neighboring intervertebral discs. The lumbar plexus lies between the two layers.
The iliacus and psoas major form the iliopsoas, which is surrounded by the iliac fascia. The iliopsoas runs across the iliopubic eminence through the muscular lacuna to its insertion on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliopectineal bursa separates the tendon of the iliopsoas muscle from the external surface of the hip joint capsule at the level of the iliopubic eminence. The iliac subtendinous bursa lies between the lesser trochanter and the attachment of the iliopsoas.
Variation
In fewer than 50 percent of human subjects, the psoas major is accompanied by the psoas minor.
One study using autopsy data found that the psoas major muscle is substantially thicker in men of African descent than in Caucasian men, and that the occurrence of the psoas minor is also ethnically variant, being present in most of the white subjects and absent in most of the black subjects.
In mice, it is mostly a fast-twitching, , while in human it combines slow and fast-twitching fibers.
Functions
Eccentric Antagonist Functions
- Restrains thigh extension and pelvic posterior tilt at the hip joint.
- Restrains thigh medial rotation and pelvic ipsilateral rotation at the hip joint.
- Restrains lumbar spinal extension.
- Restrains lumbar spinal lateral flexion to the opposite side.
- Restrains ipsilateral rotation of the lumbar spine.
- Restrains anterior tilt and depression of the same-side pelvis at the LS joint.
Note
A force of lateral rotation of the thigh at the hip joint prevents medial rotation of the entire lower extremity (thigh, leg, and talus) if the weight-bearing foot overly pronates (if the arch of the foot drops).
Isometric Stabilization Functions
- Stabilizes the lumbar spine at the spinal joints.
- Stabilizes the pelvis at the LS and hip joints.
- Stabilizes the thigh at the hip joint.
Note
Because the psoas major lies so close to the lumbar spine, its major stabilization function is at the spine.
Palpation
- With the client supine with a pillow under the knees, place palpating hand on the abdomen between the iliac crest and the twelfth rib (lateral to the rectus abdominis, approximately halfway between the ASIS and the umbilicus).
- Palpate slowly but deeply with even pressure directed posteromedially toward the spine.
- Ask the client to flex the thigh at the hip joint a few degrees and feel for the contraction of the psoas major.
- The distal belly of the psoas major is also palpable in the proximal anterior thigh between the pectineus and the sartorius. Note: Be careful with palpation in this region because the femoral nerve, artery, and vein lie over the iliopsoas and pectineus here.